The human body is full of astonishing facts that highlight your incredible design. Did you know your gut boasts around 100 million neurons? That's more than in your spinal cord! It communicates with your brain, influencing mood and digestion. Your vascular system stretches over 100,000 miles, enough to circle the Earth four times. You also shed about 30,000 skin cells every minute, totaling eight pounds annually! Plus, your liver can regenerate up to 80% of its mass. These insights only scratch the surface of your body's wonders. Keep exploring, and you'll uncover even more amazing truths about yourself!
Key Takeaways
- The human gut contains approximately 100 million neurons, functioning independently and influencing digestion and emotional behavior through gut-brain communication.
- The cornea, a transparent and avascular tissue, contributes about 70% of the eye's focusing power, essential for clear vision.
- The body sheds about 30,000 dead skin cells every minute, renewing the skin and protecting against environmental factors.
- The liver can regenerate up to 80% of its mass after surgery, showcasing its remarkable regenerative capabilities.
- The human vascular network spans over 100,000 miles, with blood vessels enabling critical functions like nutrient transport and thermoregulation.
Unique Nervous System of the Gut
The gut isn't just about digestion; it houses a unique nervous system often called the "second brain." With around 100 million neurons, this complex network operates independently from your central nervous system, playing an indispensable role in how your body functions.
This fascinating fact about the human body shows how your gut communicates with your brain, influencing everything from digestion to emotional behavior. Recent studies suggest that maintaining a healthy weight can also support gut health, which may further enhance its role in our overall well-being, especially when considering recommended nutrition plans to aid in weight management.
Did you know that the gut microbiome produces about 95% of the body's serotonin? This crucial neurochemical greatly impacts mood regulation and mental health. This connection highlights the amazing things your gut does, affecting neural development and overall well-being.
Stress responses and emotional stability are also swayed by the vagus nerve, which links your gut and brain, showcasing how interconnected our bodily functions really are.
The average person experiences these interactions every hour, as the gut continues to send signals that keep us balanced.
So, the next time you think about your body, remember that it's not just about skin cells every day or the heart beats end to end; the gut's second brain is working hard, too.
Isn't it incredible how our bodies manage such complex systems?
Extensive Vascular Network
An astonishing aspect of the human body is its extensive vascular network, which spans over 100,000 miles. This intricate system of arteries, veins, and capillaries is fundamental for your survival and plays a significant role in maintaining overall wellness through proper nutrient distribution and waste removal.
In fact, if you laid out all the blood vessels in an adult, they could circle the Earth four times, given the planet's circumference of about 25,000 miles.
Capillaries alone make up approximately 80% of this total blood vessel length, playing a pivotal role in nutrient and gas exchange at the cellular level. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from your heart, delivering the crucial oxygen and nutrients your body needs, while healthy lifestyle changes can further enhance cardiovascular health.
Meanwhile, veins return oxygen-poor blood back to the heart, ensuring proper circulation.
Beyond transporting blood, your vascular system is essential for thermoregulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal. It keeps your body functioning effectively, maintaining a delicate balance that supports everything from your daily activities to your organ health.
Skin Cell Shedding

Did you know your skin constantly renews itself? As you shed about 30,000 dead skin cells every minute, factors like age, environment, and health can influence how quickly this happens.
Regular practices like gentle yoga stretches can enhance circulation and promote skin health.
Understanding the importance of skin renewal can help you appreciate the role your skin plays in overall well-being.
Importance of Skin Renewal
Regularly shedding skin cells is fundamental for skin health and overall well-being. Your body sheds about eight pounds of dead skin annually, a process that contributes to household dust while highlighting the continuous renewal of your skin. Did you know that you lose over 30,000 dead skin cells every minute? This rapid turnover is essential for maintaining healthy skin.
Curiously, just like how cats exhibit signs of attachment, our bodies also rely on consistent renewal to maintain their protective barriers.
Every month, your entire skin surface gets replaced, ensuring that damaged or old cells are removed. This shedding process is critical for protecting you against pathogens and environmental factors, as it helps reinforce your skin barrier. A well-functioning skin barrier is your first line of defense against harmful invaders, keeping your body safe.
Curiously, dead skin cells also play a role in reducing air pollution. They contain squalene, which can lower indoor ozone levels by up to 15%. Consequently, not only does skin renewal keep you looking fresh and healthy, but it also contributes positively to your immediate environment.
Factors Influencing Shedding Rates
While various factors impact skin cell shedding rates, age is one of the most significant. As you get older, your skin's renewal process slows down, affecting how quickly you shed those dead skin cells. On average, your body sheds about 30,000 to 40,000 skin cells every minute, which adds up to roughly eight pounds a year.
Other factors also play a role in shedding rates. Environmental conditions like humidity and temperature can influence how your skin behaves. For instance, dry air can lead to increased flaking and dryness. Additionally, specific skin conditions, such as psoriasis and eczema, can escalate skin cell turnover, resulting in enhanced shedding compared to healthy skin.
Here's a quick overview of the factors influencing skin cell shedding:
| Factor | Impact on Shedding | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Slower renewal process | Older adults shed less |
| Environmental | Affects moisture levels | Dry climates increase flaking |
| Skin Conditions | Accelerated turnover | Psoriasis increases shedding |
| Diet | Nutritional impact | Poor diet may worsen skin |
| Hydration | Affects skin moisture | Dehydrated skin flakes more |
Understanding these factors can help you maintain healthier skin.
Blood Vessel Composition
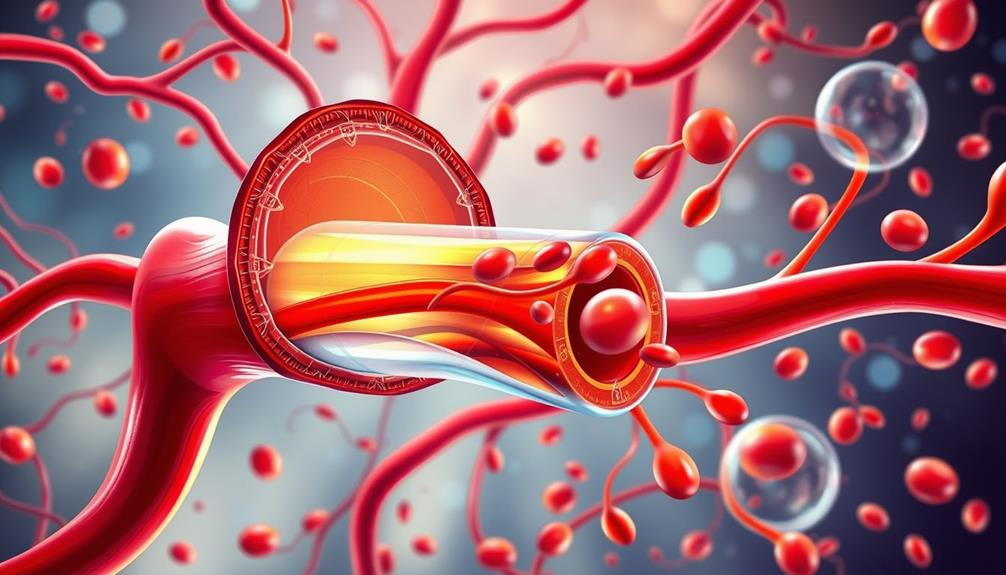
The human body boasts approximately 100,000 miles of blood vessels, creating a complex network that plays an essential role in circulation. This intricate system includes arteries, veins, and capillaries, with capillaries making up about 80% of the total length.
These smallest vessels are critical for nutrient and gas exchange at the cellular level, ensuring your body's cells receive what they need to function effectively. Interestingly, just as maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for your overall health, keeping your blood vessels healthy is essential for proper circulation and nutrient delivery, akin to how regular brushing and flossing eliminate food particles and bacteria.
Blood vessels are composed of three distinct layers: the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa. The tunica intima is the innermost layer, providing a smooth surface for blood flow. The tunica media, the middle layer, contains smooth muscle that allows the vessel to adjust its diameter.
Finally, the tunica externa, the outermost layer, offers structural support and protection.
Your blood vessels are incredibly adaptable, responding to changes in blood flow and pressure. Through processes like vasodilation and vasoconstriction, they regulate circulation and maintain homeostasis.
Remarkably, the total length of your blood vessels is nearly enough to circle the Earth four times, a staggering feat that highlights the complexity of your body's circulatory system.
Cornea's Unique Characteristics

A essential part of your eye, the cornea is a transparent, avascular tissue that allows light to enter and reach the retina, making it indispensable for clear vision. This remarkable structure comprises five layers, with the outermost layer known as the epithelium, which regenerates quickly to maintain corneal integrity.
Its unique curvature helps refract light, contributing approximately 70% of the eye's total focusing power. Notably, just as understanding personality traits can enhance self-awareness, recognizing the importance of eye health can lead to better overall well-being the effectiveness of personality tests.
Within the cornea, specialized cells called keratocytes play a significant role. These cells help maintain transparency and structural integrity by regulating hydration levels within the cornea. Without proper hydration, the cornea can become cloudy, impairing your vision.
Damage to the cornea, such as scarring or clouding, can greatly affect your ability to see clearly. In such cases, medical intervention may be necessary to restore clarity. This could involve procedures like a corneal transplant, highlighting just how essential the cornea is to your overall vision.
Understanding these unique characteristics of the cornea emphasizes its importance in daily life, reminding you to care for your eye health to maintain clear and sharp vision throughout your life.
Gut Bacteria and Mood
Understanding how your body functions goes beyond just eye health; it extends into the intricate relationship between your gut and your mood.
Your gut is home to about 100 trillion bacteria, which play a significant role in influencing your emotional behavior. Surprisingly, around 95% of the serotonin, a key neurotransmitter that regulates your mood, is produced in the gut. This highlights the direct connection between gut health and mental well-being.
Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet rich in vegan protein sources can further support a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for ideal emotional health.
Research has shown that gut bacteria can affect your brain chemistry and even neural development, suggesting that what's happening in your digestive system can impact your emotional stability.
When there's an imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, it's been linked to conditions such as anxiety and depression. This makes maintaining a healthy gut microbiome essential.
To support your mood, consider incorporating probiotics and a fiber-rich diet into your meals. These can promote a diverse gut microbiome, potentially leading to improved mood and cognitive function.
Heart Rate and Music

Your heart rate doesn't just respond to exercise; it reacts to the music you listen to as well.
Research indicates that AI-generated music can evoke specific emotional responses, further influencing your heart rate variability. The tempo and emotional impact of a song can affect your overall physiological state.
Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability (HRV) plays an essential role in how your body responds to stress and changes in the environment. It refers to the fluctuations in the time intervals between your heartbeats, reflecting your body's ability to adapt. Research shows that listening to music can notably impact your HRV. When you listen to calming music, you often experience increased variability, suggesting relaxation and improved function of your autonomic nervous system.
Understanding safe foods can also contribute to overall wellness, influencing how your body manages stress and health. Engaging with music doesn't just soothe your mind; it can lower your heart rate, enhancing HRV by promoting a state of relaxation and reducing stress.
Curiously, the tempo of the music you choose can directly affect your HRV. Slower tempos are more likely to boost HRV, while fast-paced music may decrease variability, causing your heart rate to rise.
Monitoring your HRV can give you valuable insights into your cardiovascular health. Higher HRV is typically associated with better fitness levels, effective recovery from stressors, and lower overall stress.
Music's Physiological Effects
The powerful connection between music and physiological responses can be truly captivating. You mightn't realize it, but the music you listen to can greatly impact your heart rate.
Research shows that fast-paced music can elevate your heart rate by up to 20%. This tempo can even influence your physical performance, enhancing exercise efficiency and increasing workout intensity by synchronizing your movements. Notably, just as music can energize you, certain beverages like mushroom coffee also promote focus and energy, offering unique health benefits that can complement your active lifestyle mushroom coffee benefits.
Consider these effects of music on your heart rate:
- Fast music increases heart rate, energizing you for workouts.
- Synchronized rhythms improve mood and elevate energy levels.
- Slow, calming music lowers heart rates and reduces anxiety.
- Music therapy can enhance cardiovascular health through improved heart rate variability.
When you listen to faster tracks, your heartbeat naturally aligns with the tempo, creating a more synchronized cardiovascular response.
On the flip side, slow music promotes relaxation, which can lead to lower blood pressure. By understanding these physiological effects, you can use music to enhance your mood, boost your workouts, or simply unwind after a long day.
Embracing the power of music can be a game-changer for your overall well-being.
Brain Changes During Pregnancy

Pregnancy triggers remarkable changes in the brain that enhance a mother's ability to connect with her newborn. During this transformative period, your brain experiences significant reductions in cortical thickness and surface area in grey matter, especially in areas linked to social cognition and emotional processing.
These alterations are thought to improve your ability to interpret your infant's needs and foster bonding, showcasing an evolutionary adaptation. Additionally, caregiver support resources can play an essential role in helping new mothers navigate these changes and provide care for their newborns effectively.
Research shows that these neural modifications can stick around for at least two years postpartum, indicating long-lasting effects on your maternal behavior. The changes in your cerebral cortex sharpen your efficiency in processing social situations and recognizing potential threats, critical skills for nurturing instincts.
A study published in *Nature Neuroscience* highlights that these brain changes aren't just structural; they're functional too. They contribute to improved maternal responsiveness, allowing you to react more effectively to your baby's cues.
This means your brain isn't only adapting but also enhancing your ability to create a deep, intuitive connection with your child. Embracing these changes can lead to a more fulfilling and responsive parenting experience.
Bone Fusion Over Time
As you grow, your body undergoes a fascinating process of bone fusion that shapes your skeleton.
You start with about 300 bones at birth, but by adulthood, that number drops to 206 as certain bones merge, especially in the skull.
This fusion not only provides stability but also impacts your mobility and overall skeletal health.
Bone Growth Process
From birth to adulthood, your bones undergo a fascinating transformation through a process known as bone fusion. Initially, you're born with about 300 bones, many made of cartilage. As you grow, some of these bones gradually fuse together, resulting in a total of 206 bones by the time you reach adulthood. This fusion is particularly evident in your skull, where several bones merge to form a solid structure.
Key aspects of the bone growth process include:
- Growth Plates: Located at the ends of long bones, they're crucial for lengthening during childhood and close as you mature.
- Fusion Patterns: Different bones fuse at various stages, contributing to your unique skeletal structure.
- Bone Density: You typically have denser bones when you're younger, which decreases over time, raising the risk of fractures.
- Adaptation: Your bones adapt to stress and strain, strengthening in response to physical activity.
Understanding this process highlights the incredible ability of your body to develop and adapt as you grow, ensuring that your skeletal system supports you throughout life.
Fusion in Adulthood
Understanding how bone fusion continues into adulthood reveals important insights into your skeletal health. At birth, you start with around 300 bones, but as you grow, this number decreases to 206. This reduction primarily occurs in the skull, where small bones fuse to create a single, stronger structure.
The fusion process isn't just limited to the skull; it also involves the growth plates in your long bones. These plates, which consist of developing cartilage, close during late adolescence, marking the end of your bone lengthening and further fusion.
Throughout your early adulthood, your bone density increases, peaking in your early 30s. After that, you might notice a gradual decline, especially if you're a woman going through menopause due to hormonal changes. This decline can make you more susceptible to bone-related issues later in life.
Understanding the nuances of bone fusion and development is essential for identifying potential problems related to bone health and growth disorders in younger individuals, allowing for early intervention if necessary.
Taking care of your bones now can pay off greatly in your later years.
Impact on Mobility
Bone fusion considerably influences your mobility throughout life. At birth, you have around 300 bones, but as you grow, many of these bones fuse, leaving you with just 206 bones in adulthood. This fusion primarily happens at growth plates, which close by the end of adolescence.
The resulting stability and strength of your skeleton are crucial for maintaining mobility and engaging in physical activities.
As you age, bone density changes, peaking in early adulthood before gradually declining. This decrease can impact your movement and overall mobility. The structural changes in your skeletal system, including the process of bone fusion, play a significant role in supporting your body's movements and posture.
Here are some key impacts of bone fusion on mobility:
- Increased stability and strength in the adult skeleton
- Improved ability to perform physical activities
- Crucial support for maintaining posture
- Potential mobility challenges as bone density decreases with age
Understanding these factors can help you appreciate the importance of bone health and mobility throughout your life.
Liver Regeneration Ability
The liver stands out as the only organ in your body that can regenerate itself, an extraordinary ability that allows it to recover even after considerable surgical removal. If you were to undergo a partial hepatectomy, your liver could regrow up to 80% of its mass within just a few weeks.
This rapid regeneration is primarily driven by hepatocytes, the main functional cells in your liver, which divide quickly in response to injury or tissue loss.
This remarkable capability is essential for maintaining critical functions like detoxification, metabolism, and bile production, all of which are fundamental for your overall health and homeostasis.
However, factors such as age, health status, and the presence of liver diseases can greatly influence how well your liver regenerates. This highlights the importance of taking care of your liver through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
Daily Mucus Production

While liver regeneration showcases your body's remarkable ability to heal, another unseen yet significant process is happening daily: mucus production. Your nose produces about one cup of mucus each day, playing an essential role in your respiratory health. This slimy substance traps pathogens and particles, protecting your lungs from potential harm.
Mucus isn't just a protective barrier; it also helps maintain moisture levels in your nasal passages. Its consistency can change based on your hydration and health status, impacting its effectiveness. If you notice excessive mucus, it might signal allergies or infections that require attention.
Here are some key functions of daily mucus production:
- Traps pathogens: Prevents harmful substances from entering your respiratory system.
- Maintains moisture: Keeps nasal passages hydrated, reducing discomfort.
- Indicates health issues: Excess mucus can point to allergies or infections.
- Protects against irritants: Shields your lungs from environmental pollutants.
Understanding mucus production helps you appreciate this essential process, keeping your respiratory system safe and functioning effectively.
Sweat Composition and Function

When you sweat, your body relies on different types of glands to release a mix of water, salts, and waste products.
This combination not only helps cool you down but also maintains your body's electrolyte balance.
Understanding the composition and function of sweat can shed light on how your body regulates temperature during various activities.
Sweat Gland Types
Sweat glands play an essential role in regulating your body temperature and maintaining overall homeostasis. There are two main types of sweat glands in your body: eccrine and apocrine.
Eccrine glands are distributed throughout most of your skin and primarily help cool you down by releasing a watery, salt-based sweat. These glands kick into gear during physical activity or when you're feeling overheated.
On the other hand, apocrine glands are mostly found in areas with hair follicles, like your armpits and groin. They produce a thicker, milky sweat and generally activate during emotional stress or sexual arousal.
Here are some key points about sweat glands:
- Eccrine glands: Regulate body temperature through watery sweat.
- Apocrine glands: Produce thicker sweat linked to emotions and hormones.
- Activation: Eccrine glands respond to heat; apocrine glands respond to stress.
- Sweat pores: You have around 2.5 million, with sweat production varying based on genetics and environment.
Understanding how these glands function can give you insight into your body's cooling mechanisms and overall health.
Composition of Sweat
The composition of sweat is essential for your body's ability to regulate temperature and maintain balance. Sweat is made up of about 99% water, with the remaining 1% containing salts, urea, and other waste products. This unique blend plays a significant role in regulating your body's temperature and keeping your electrolyte levels in check.
The primary salts in sweat are sodium and chloride, which help maintain fluid balance and support nerve function. When you engage in physical activities, your sweat production can increase dramatically—averaging between 0.8 to 1.4 liters per hour in high temperatures.
Your body relies on two types of sweat glands: eccrine glands, which are found all over your skin and primarily help regulate temperature, and apocrine glands, located in specific areas, contributing to body odor.
Notably, the composition of your sweat can vary based on diet, hydration levels, and individual physiology. These factors can influence the concentration of electrolytes and other components in your sweat, showcasing the dynamic nature of your body's processes.
Understanding sweat composition highlights its essential role in your overall health and well-being.
Temperature Regulation Role
During physical activity or on a hot day, your body relies on sweating to maintain a stable internal temperature. You have about 2.5 million sweat pores, mainly controlled by eccrine sweat glands, which are essential for thermoregulation. When your body heats up, these glands kick into action, producing sweat that evaporates from your skin, helping to cool you down.
Here are some key points about sweat's role in temperature regulation:
- Composition: Sweat is mostly water, but it also contains salts, waste products, and fatty acids.
- Production: You can produce 1 to 2 liters of sweat daily, and even more during intense exercise or in hot conditions.
- Eccrine vs. Apocrine: Eccrine glands are your body's main sweat producers for cooling, while apocrine glands respond to stress and emotional triggers.
- Adaptability: Your body quickly adapts to temperature changes by increasing sweat production, ensuring effective temperature regulation.
Understanding how sweat works helps you appreciate your body's remarkable ability to stay cool and balanced, even in challenging conditions.
Fluctuating Height Throughout the Day

Throughout the day, you can experience a height change of up to half an inch due to the natural compression of your spinal discs. When you wake up in the morning, you're typically about 1 cm taller. This increase is a result of your spinal discs rehydrating overnight, allowing them to expand.
However, as the day progresses, gravity takes its toll. Your spinal cartilage compresses under the weight of your body, leading to a gradual loss of height. By the end of the day, it's common for adults to lose around half an inch (1.27 cm). This fluctuation is a normal physiological response and can vary from person to person.
If you spend long hours standing or sitting, you might notice that your height reduction is more pronounced. This is because the pressure on your spine increases during those prolonged positions.
Average Walking Distance

Walking an average of 3 to 4 miles per hour, you can cover significant distances with relative ease.
Imagine if you walked for 12 hours every day; it would take you about 690 days to circumnavigate the globe, traveling roughly 24,901 miles. Over your lifetime, the distance you walk can add up to several thousand miles, depending on your lifestyle and activity levels.
Not only is walking a basic form of transportation, but it also offers numerous health benefits.
Here are some key points to reflect on:
- Cardiovascular health: Regular walking strengthens your heart and improves circulation.
- Mood enhancement: Walking releases endorphins, boosting your mood and reducing stress.
- Improved fitness: It helps maintain a healthy weight and increases overall endurance.
- Chronic disease reduction: Incorporating walking into your routine lowers the risk of many chronic illnesses.
Toilet Time Habits

Most people don't realize just how much time they spend in the bathroom. On average, you might find yourself sitting on the toilet for about a year of your life! This considerable amount of time underlines how essential toilet habits are in your daily routine. Your habits can vary widely due to culture, diet, and personal health, all of which influence how long you spend in the restroom.
Regular bathroom breaks are critical for urinary health, helping your body eliminate waste and maintain proper bladder function. Factors like hydration levels and digestive health can greatly impact both the time you spend and how often you visit the toilet. If you're well-hydrated, you might find yourself taking more frequent trips, while a balanced diet can lead to quicker bathroom breaks.
Moreover, your personal habits regarding toilet time can greatly affect your overall comfort and well-being. Managing this aspect of your health is essential, as it can improve your daily life.
Conclusion
In exploring these mind-blowing facts about the human body, you realize just how intricate and fascinating you truly are. From your gut's unique nervous system to the way you shed skin cells, each aspect plays a crucial role in your overall health. As the saying goes, "You don't know what you've got 'til it's gone." Appreciate your body's wonders now, as they work tirelessly behind the scenes, keeping you vibrant and alive every day.










